In this article, we will explore the concept of evaporation and examine the Factors Affecting Evaporation.
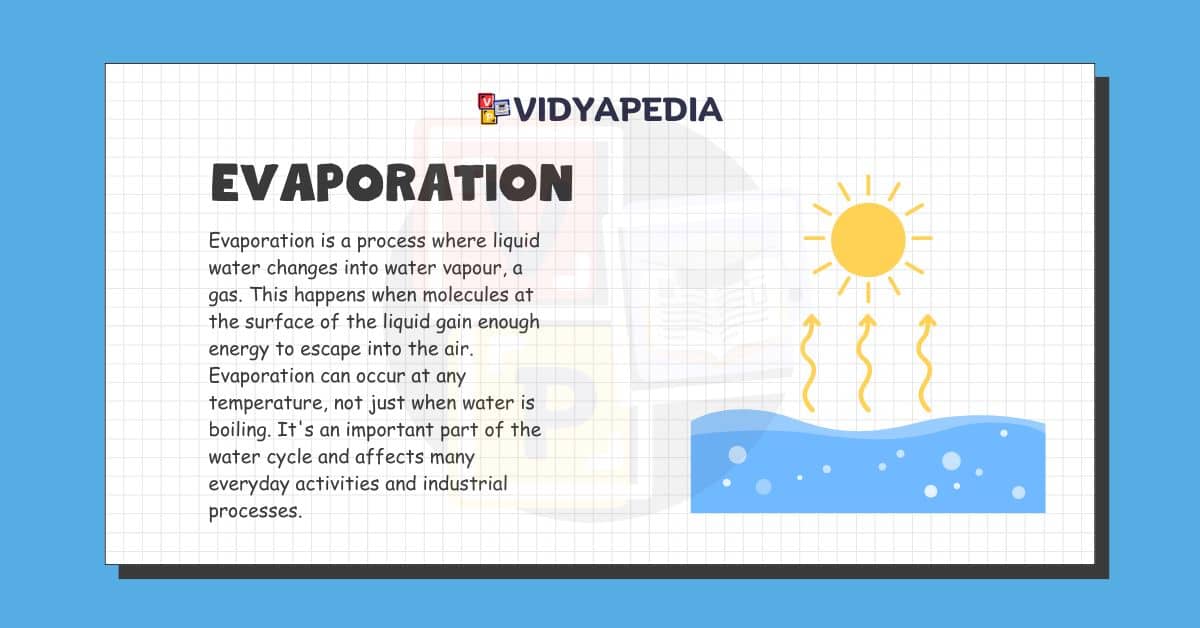
Evaporation is a process where liquid water changes into water vapour, a gas. This happens when molecules at the surface of the liquid gain enough energy to escape into the air. Evaporation can occur at any temperature, not just when water is boiling. It’s an important part of the water cycle and affects many everyday activities and industrial processes.
Read Related Topic: Change Of State Of Matter
Introduction Of Matter and Physical Properties
Main Factors That Affect Evaporation

Temperature
Higher Temperature: When the temperature is higher, the molecules in the liquid move faster. This increased movement gives some molecules enough energy to break free from the liquid’s surface and become vapour. For example, on a hot day, puddles dry up quickly because the water evaporates faster.
Lower Temperature: When the temperature is lower, the molecules move more slowly and have less energy. This means fewer molecules can escape the liquid, and evaporation happens more slowly. For instance, a wet cloth takes longer to dry on a cold day.
Surface Area
Larger Surface Area: If a liquid has a larger surface area exposed to air, more molecules can escape at once, speeding up evaporation. Imagine spreading out a wet towel versus keeping it folded. The spread-out towel dries faster because more water molecules are exposed to the air.
Smaller Surface Area: With a smaller surface area, fewer molecules can escape, slowing down evaporation. A folded towel dries much slower for this reason.
Humidity
Lower Humidity: When the air is dry and contains little water vapour, it can absorb more water from the liquid, increasing the rate of evaporation. Clothes dry faster in dry weather because the air can take in more moisture.
Higher Humidity: When the air is already full of water vapour(high humidity), it can’t absorb much more, which slows down evaporation. This is why drying clothes takes longer on a humid day.
Wind Speed
Higher Wind Speed: Wind blows away the moist air near the surface of the liquid and replaces it with drier air. This helps evaporation happen faster. For example, clothes dry quickly on a windy day because the wind removes the moist air around them.
Lower Wind Speed: When the air is still, the moisture stays near the surface of the liquid, slowing down evaporation. Clothes take longer to dry on a calm day for this reason.
Nature of the Liquid
Volatile Liquids: Some liquids evaporate faster because their molecules need less energy to escape into the air. Examples include alcohol and acetone, which evaporate quickly even at room temperature.
Non-volatile Liquids: Other liquids, like water and glycerin, need more energy to evaporate and do so more slowly.
Pressure
Lower Atmospheric Pressure: When the air pressure is low, it is easier for the molecules to escape from the liquid to the air. This means evaporation happens faster. For example, water boils and evaporates quicker at high altitudes where the air pressure is lower.
Higher Atmospheric Pressure: High air pressure makes it harder for the molecules to escape, so evaporation happens more slowly. This is why boiling takes longer at sea level where the pressure is higher.
Presence of Solutes
Solutes like Salt or Sugar: Adding substances like salt or sugar to water lowers its vapour pressure. This means fewer water molecules can escape into the air, which slows down evaporation. This principle is used in making salt solutions to preserve food, as it reduces water loss through evaporation.
Practical Examples
Drying Clothes: Clothes dry faster on warm, windy days because higher temperatures and wind speeds increase evaporation.
Cooling Effect of Sweat: When we sweat, the liquid sweat evaporates from our skin, taking heat away and cooling our bodies.
Industrial Processes: Evaporation is used in industries for processes like distillation (separating mixtures based on boiling points), drying (removing moisture from products), and concentrating solutions (like making concentrated fruit juices).